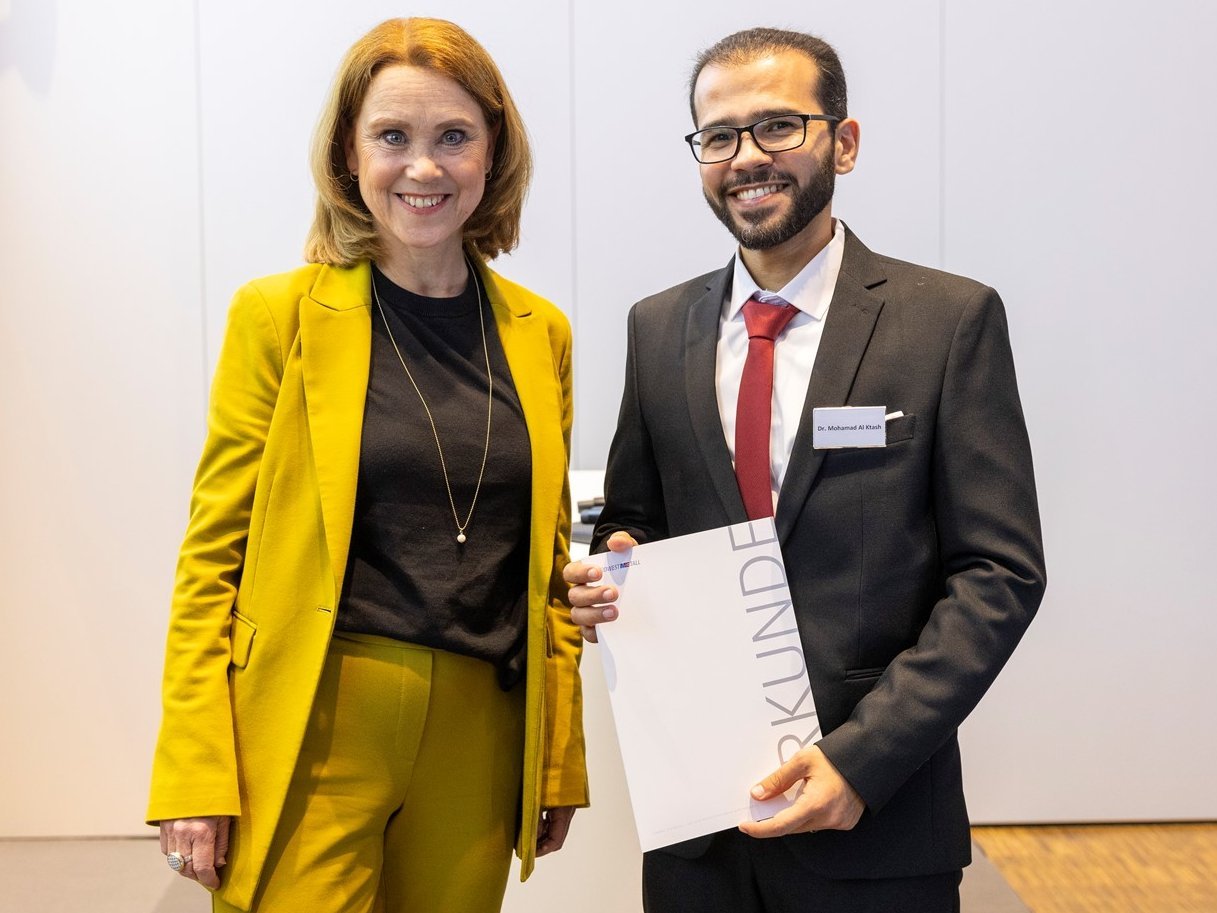
Südwestmetall Sponsorship Award 2025 honors interdisciplinary cutting-edge research
Dr. Mohammad M. Al Ktash from Reutlingen University and employee of the PAT Centre has been awarded the 2025 Sponsorship Prize of the Südwestmetall employers' association for his excellent dissertation “Development of a UV Hyperspectral Imaging Prototype for Industrial Applications”.